Understanding payroll accounting is crucial for maintaining financial integrity and ensuring compliance with legal and tax obligations. Payroll accounting involves tracking and recording all payroll-related transactions, including employee paychecks, taxes, deductions, and employer contributions. Accurate payroll accounting ensures timely and correct employee payments and maintains an organization’s financial health. Let’s dive into the key components of payroll accounting and how to avoid common pitfalls.
Setting Up the Chart of Accounts
Before you can begin recording payroll, setting up the appropriate accounts in the chart of accounts is essential. These typically include:
- Expense accounts: For wages, employer-paid benefits, and the employer’s portion of taxes.
- Liability accounts: For amounts deducted from employee paychecks and temporarily held before remittance.
Account Mapping
Once the chart of accounts is set up, the next crucial step is mapping the pay items to the correct accounts. This process ensures that each specific pay item is recorded accurately within the chart of accounts, whether you’re processing payroll within accounting software or entering payroll journal entries manually.
Gathering Essential Reports
To create accurate payroll journal entries, you’ll need to collect key documents:
- Payroll Register: This comprehensive report details all payroll transactions during the pay period, including employee names, pay dates, and payment amounts. It may also include quarter-to-date and year-to-date totals.
- Payroll Tax Liability Report: This report provides a breakdown of taxes owed by the business and taxes withheld from employee paychecks.
- Deductions Register: This document outlines employee deductions from gross wages that must be paid to third parties, such as taxes, health insurance premiums, retirement account deferrals, child support, or garnishments.
Journal Entries
Payroll journal entries typically involve debiting gross wage expenses and crediting various liabilities. Remember, employer contributions and taxes should be recorded as both expenses and liabilities until paid.
Here is a simple example:
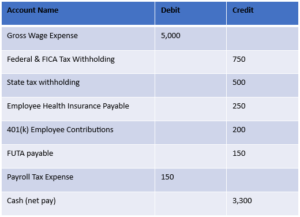
Avoiding Common Payroll Accounting Errors
To maintain accurate records and ensure compliance, be vigilant about these common errors:
- Over or underpayment of payroll taxes
- Failing to record employer benefit contributions as expenses
- Incorrectly applying benefit payments entirely to expense accounts
- Misconfigured payroll account mapping in software systems
Conduct monthly reviews of the balance sheet to ensure liability accounts are zeroing out appropriately and payments are applied to the correct accounts. Perform quarterly reviews of payroll activities to identify and address potential issues promptly. Compare monthly payroll expenses and verify that tax expense accounts align with payroll reports.
Mastering payroll accounting is essential for a business’s financial health. By understanding the key components, avoiding common errors, and implementing best practices, you can ensure accurate financial reporting and compliance with tax obligations. At Yeo & Yeo, we’re committed to helping businesses navigate the complexities of payroll accounting. For personalized guidance on optimizing your payroll processes, contact our team.

